Why Is Mold Manufacturing Essential for Quality Product Development?
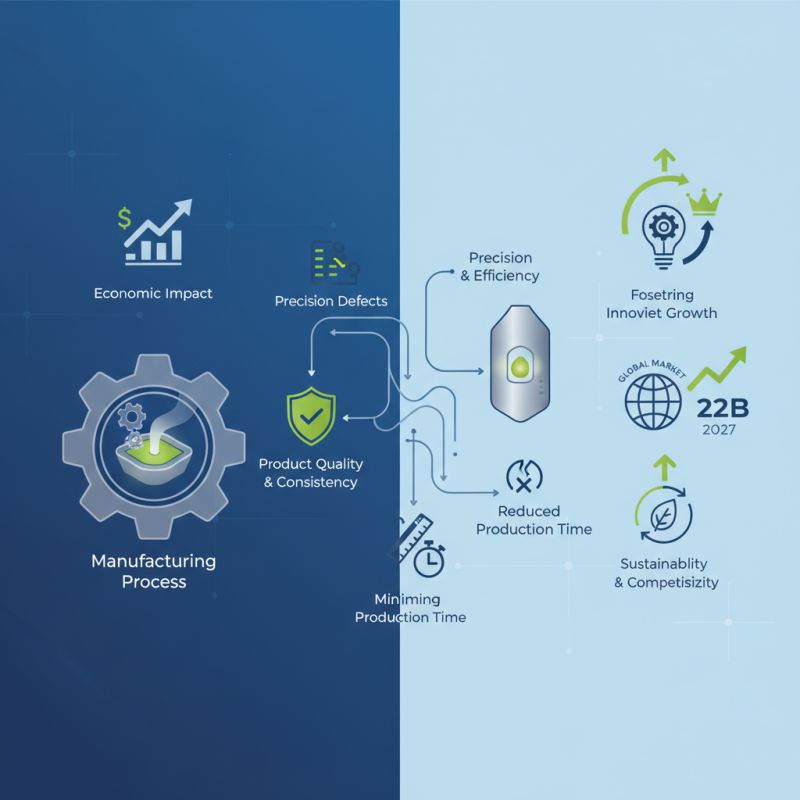
Mold manufacturing plays a pivotal role in the realm of product development, serving as a crucial step in transforming innovative concepts into tangible items. According to a report by the Plastics Industry Association, the plastic mold manufacturing sector contributes approximately $5 billion to the U.S. economy annually and supports thousands of jobs across various states. This highlights not only the economic significance of mold manufacturing but also its fundamental importance in ensuring product quality and consistency.
The precision and efficiency provided by advanced mold manufacturing techniques directly influence the performance and reliability of final products. The Global Industry Analysts report indicates that the global market for molds is projected to reach $22 billion by 2027, underlining the importance of this manufacturing process in the ever-evolving landscape of product development. By utilizing state-of-the-art technology and skilled craftsmanship, businesses can minimize defects, reduce production time, and ultimately deliver high-quality products that meet consumer expectations. As industries increasingly emphasize sustainability and adaptability, mold manufacturing will continue to be an essential element in fostering innovation and ensuring that companies remain competitive in a demanding market.
The Role of Mold Manufacturing in Product Development
Mold manufacturing plays a critical role in the product development process, serving as the backbone for numerous industries including automotive, consumer goods, and medical devices. According to a report by the American Society for Quality, effective mold manufacturing can reduce production costs by up to 30% while significantly enhancing the precision and quality of end products. This highlights the importance of integrating advanced mold-making techniques, such as computer numerical control (CNC) machining and additive manufacturing, which accelerate the prototyping phase and foster innovation.
In product development, molds are not merely tools; they are vital contributors to design feasibility and manufacturability. A study conducted by the Society of Plastics Engineers indicates that around 70% of product failures can be traced back to design flaws, often originating in the mold manufacturing stage. By employing advanced simulation software and rapid prototyping techniques, manufacturers can test and iterate on designs before mass production, minimizing the risk of costly errors. This iterative process not only ensures better quality control but also shortens time-to-market, a crucial factor in today's competitive landscape. As such, mold manufacturing is not just a manufacturing step; it is an essential strategy for achieving high-quality product development.
Understanding the Mold Manufacturing Process and Its Impact on Quality
The mold manufacturing process plays a crucial role in ensuring the quality of end products across various industries. At its core, mold manufacturing involves creating molds that shape and form materials into desired products. This process requires precision engineering, as even minor imperfections in mold design can lead to defects in the final product. High-quality molds facilitate accurate replication of product designs, which is vital for consistency and reliability in mass production. Additionally, the materials used in mold manufacturing, such as high-grade steel or aluminum, impact not only the durability of the molds but also the quality of the products produced.
Moreover, the intricacies of the mold-making process, including machining, finishing, and testing, directly influence the efficiency and effectiveness of production. Advanced techniques, such as computer-aided design (CAD) and computer numerical control (CNC) machining, enhance the accuracy of mold creation, allowing for more complex and innovative product designs. The cooling and heating characteristics of molds also affect cycle time and product integrity, which highlights the necessity of meticulous design and execution. Hence, a well-executed mold manufacturing process not only optimizes production efficiency but also contributes significantly to the durability, performance, and aesthetic appeal of the final products.
Importance of Mold Manufacturing in Quality Product Development
This chart illustrates key quality factors in the mold manufacturing process, showing their significance for product development. High precision and durability are crucial for ensuring the final product meets quality standards, while surface finish and production speed also play important roles in the overall efficiency and effectiveness of product manufacturing.
Key Advantages of High-Quality Molds for Product Consistency
High-quality molds are crucial for ensuring product consistency throughout the manufacturing process. When molds are crafted with precision and superior materials, they produce parts that meet exact specifications repeatedly. This consistency not only enhances the overall quality of the final product but also minimizes variations that can lead to defects. By maintaining uniformity across production runs, companies can establish a strong reputation for reliability, which is essential in competitive markets.
Additionally, high-quality molds contribute to efficiency in the production process. When molds are designed to withstand wear and tear, they can endure longer production cycles with minimal maintenance. This durability translates to reduced downtime and lower operational costs, enabling manufacturers to meet customer demands promptly. Furthermore, precise molds can facilitate easier integration with automated systems, streamlining the manufacturing process and enhancing overall productivity.
In summary, investing in high-quality molds leads to better product consistency and manufacturing efficiency, both of which are vital for successful product development.
Challenges in Mold Manufacturing and Their Implications for Product Design
Mold manufacturing plays a critical role in the development of high-quality products, yet it is fraught with challenges that can significantly impact product design. One of the primary challenges in this process is achieving precision. Molds must be meticulously crafted to ensure they produce components that meet rigorous specifications. Even minor inaccuracies can lead to defects in the final product, necessitating costly revisions and delays. This attention to detail requires skilled workmanship, advanced technology, and thorough quality control measures, all of which can be resource-intensive.
Another significant challenge is material selection. The choice of materials used in mold manufacturing directly affects the performance and durability of the final products. Different materials can respond variably to the molding process, influencing aspects such as heat resistance, flexibility, and longevity. Designers and manufacturers must collaborate closely to ensure that the selected materials align with the intended product use and lifecycle. Any mismatch may lead to complications in production and ultimately affect customer satisfaction and marketability, underscoring the importance of rigorous testing and validation throughout the design phase. Balancing these challenges with innovative solutions is essential for successful product development and achieving competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Future Trends in Mold Technology and Their Influence on Manufacturing Quality

As industries increasingly recognize the importance of precision and efficiency, advancements in mold technology play a critical role in enhancing manufacturing quality. According to a recent report by the International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, the use of injection molds is projected to reach a market valuation of $22 billion by 2025. This growth is largely driven by innovations such as 3D printing and computer-aided design (CAD), which allow for rapid prototyping and more complex mold geometries that improve product consistency and reduce waste.
Furthermore, industry experts emphasize the impact of smart technologies on mold manufacturing. The integration of IoT (Internet of Things) in mold production enables real-time monitoring of mold conditions, which can significantly enhance maintenance practices and reduce downtime. A study from the Society of Manufacturing Engineers indicated that manufacturers utilizing predictive maintenance approaches can see a reduction in manufacturing defects by up to 30%. As these technologies evolve, they not only streamline operations but also enhance the overall quality of the final products, putting manufacturers ahead in a competitive market.
Related Posts
-

7 Compelling Reasons to Choose Advanced Mold Manufacturing for Your Production Needs
-

How to Choose the Best Injection Molding Die for Your Production Needs: Insights from Industry Experts
-
Exploring Unique Product Features and Applications in Best Plastic Injection Mold Tooling
-

Exploring the Future of Mold Manufacturing with Advanced Automation Technologies
-
Why Injection Tooling is Essential for Efficient Manufacturing Processes
-

2025 How to Master Injection Mold Making for Efficient Production
