What is the Plastic Injection Moulding Process Explained?
The plastic injection moulding process is a transformative technique in manufacturing. It allows the production of complex shapes efficiently. By injecting molten plastic into a mold, manufacturers can create precise and consistent products.
This process has many advantages. It is cost-effective for large-scale production. However, it also has its challenges. The initial setup costs can be high. Additionally, the choice of material affects the final product.
Understanding the plastic injection moulding process is crucial for industries. It provides insights into production efficiency and quality control. As technology evolves, this method will likely advance, yet it also requires careful consideration of environmental impacts.
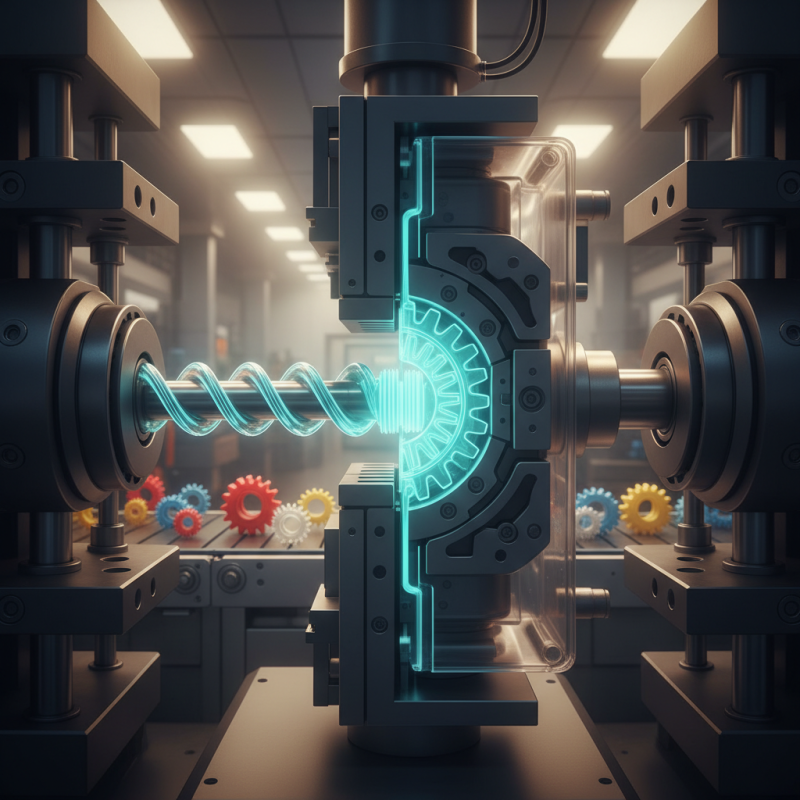
Overview of Plastic Injection Moulding Process
The plastic injection moulding process is vital in manufacturing many components. It begins with heating plastic pellets until they melt. This molten plastic is then injected into a mould under high pressure. Cooling follows, solidifying the material into the desired shape.
This method is efficient and can produce intricate designs. However, it requires precise control of temperature and pressure. A slight error can result in defects, leading to waste. The importance of quality control cannot be overstated. Even minor inconsistencies can impact product performance.
While the process is widely used, it does have its challenges. Mould design can be complex. High initial costs for mould creation often deter smaller businesses. Additionally, selecting the right plastic type for each application demands careful consideration. Overall, the plastic injection moulding process is fascinating yet complex.
Key Components of Injection Moulding Machinery
The injection moulding process relies heavily on key components of machinery. The heart of this system is the injection unit, where plastic pellets are heated. As the temperature rises, the material melts and becomes liquid. This molten plastic is injected into a mould. Precise control here is crucial for quality and consistency.
Next, the clamping unit is essential for maintaining the mould's integrity. It securely holds the mould closed during injection. If the clamps do not function properly, defects can occur. The hydraulic system provides the force needed to keep the mould tightly shut. Ineffective clamping can lead to leakage and errors in the final product.
Another important element is the cooling system. Once the plastic is injected, it must cool down to solidify. A well-designed cooling system ensures even cooling, which impacts the finished part’s durability. However, cooling times can sometimes be unpredictable. Manufacturers need to monitor this closely to avoid defects. Each component plays a significant role, and any shortcomings can lead to costly mistakes.
Step-by-Step Procedure of Injection Moulding
The injection moulding process involves several clear steps. First, the raw plastic material, usually in pellet form, is heated until it melts. This transition makes it pliable and ready for shaping. Next, the molten plastic is injected into a closed mould. This mould is precisely designed to create the desired shape of the final product.
After injection, the cooling phase begins. The mould cools down, allowing the plastic to solidify. This step is crucial as improper cooling can lead to defects. Once cooled, the mould opens, and the finished part is ejected. The entire cycle can take seconds to minutes, depending on the complexity of the part.
Tip: Always check the quality of the mould. Even minor imperfections can lead to significant flaws in the final product. Maintaining your equipment is essential to avoid production delays.
Another point to consider is the recycling of plastic waste. During production, waste material can accumulate. Finding ways to minimize this waste is vital. It can reduce costs and promote sustainability. Careful planning and design adjustments can enhance efficiency and reduce losses.
Common Materials Used in Plastic Injection Moulding
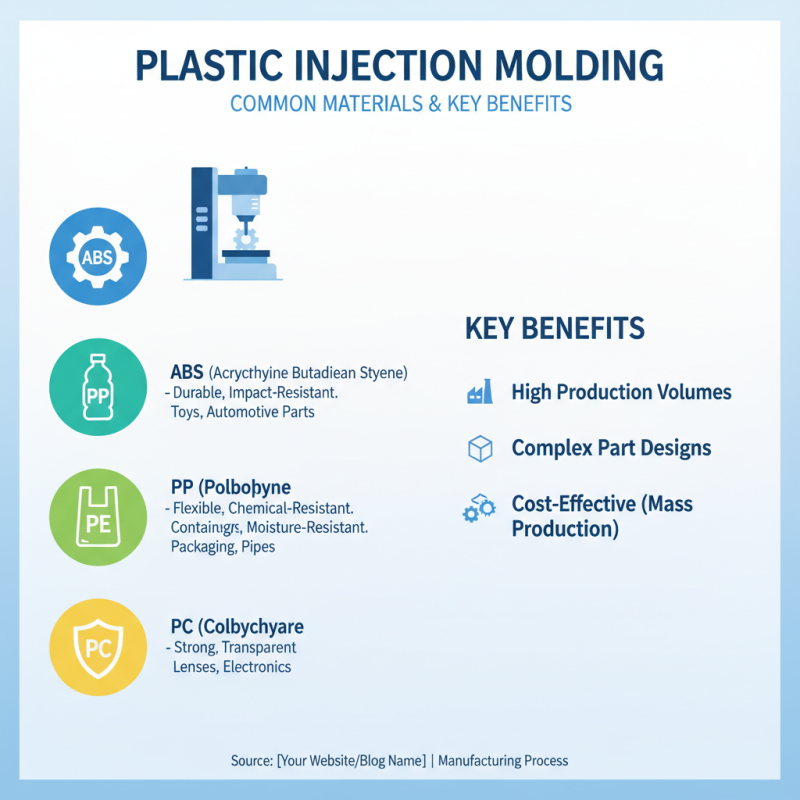
Plastic injection moulding is a widely used manufacturing process. Various materials can be employed. Here are some common ones:
1. **Polypropylene (PP)** is popular for its versatility. It is flexible and resistant to chemicals. Products made from PP include containers, automotive parts, and toys.
2. **Polyethylene (PE)** is another common choice. This material is lightweight and strong. It often appears in packaging, pipes, and bottles. PE is also recyclable, which adds environmental benefits.
3. **Polystyrene (PS)** is affordable and easy to mould. It often forms disposable cutlery, cups, and containers. However, it has low impact resistance, making it less durable.
4. **Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)** is known for its toughness. Phones and electronic housings often use it. The challenge lies in its heat sensitivity during the moulding process.
**Tips:** Always consider the final product's application. For example, choosing the right material affects durability and cost. Test samples before full production can save time and money.
**Tips:** Understand the limitations of each material. For instance, while polystyrene is cheap, it may not withstand heavy use. Prioritize the right properties for your needs.
Applications and Benefits of Injection Moulded Products
Injection moulding is widely used in various industries. This process creates precise and intricate plastic products. The efficiency of injection moulding allows for mass production, reducing costs significantly. Companies benefit from strong, lightweight components. Products range from automotive parts to consumer goods.
The environmental impact of plastic products raises concerns. However, recycling options are improving. Many manufacturers are exploring biodegradable materials. This shift could transform the industry. Injection moulded products show promise in innovation and sustainability. The demand for custom designs also drives advancements in this field.
Despite advancements, challenges remain. Quality control can be inconsistent. Some products may not meet the expected standards. Continuous improvement is necessary to achieve better results. Overall, the applications of injection moulding continue to expand, offering numerous benefits while also encouraging reflection on sustainability practices.
What is the Plastic Injection Moulding Process Explained? - Applications and Benefits of Injection Moulded Products
| Application | Material Type | Benefits | Typical Industries |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consumer Electronics | ABS, Polycarbonate | High durability, excellent finish | Electronics, Telecommunications |
| Automotive Parts | Polypropylene, Nylon | Lightweight, Resistant to chemicals | Automotive, Transportation |
| Medical Devices | Polyethylene, Polypropylene | Sterilizable, Biocompatible | Healthcare, Pharmaceuticals |
| Packaging | PET, PVC | Lightweight, Cost-effective | Food and Beverage, Consumer Goods |
| Toys | ABS, Polypropylene | Variety of colors, Safe for children | Manufacturing, Retail |
Related Posts
-
Innovative Injection Molding Design Examples to Inspire Your Next Project
-

How to Maximize Efficiency in Plastic Injection Molding: Strategies and Industry Insights
-

Exploring the Future: How Plastic Injection Molding Shapes a $300 Billion Industry
-

7 Compelling Reasons to Choose Advanced Mold Manufacturing for Your Production Needs
-
Why Injection Tooling is Essential for Efficient Manufacturing Processes
-

Common Challenges in the Best Plastic Injection Moulding Process
